- Elkem
- Products
- Foundry alloys
- Our technical advice for your processes
- Casting weight and thickness
Casting weight and thickness
Optimize casting weight and thickness
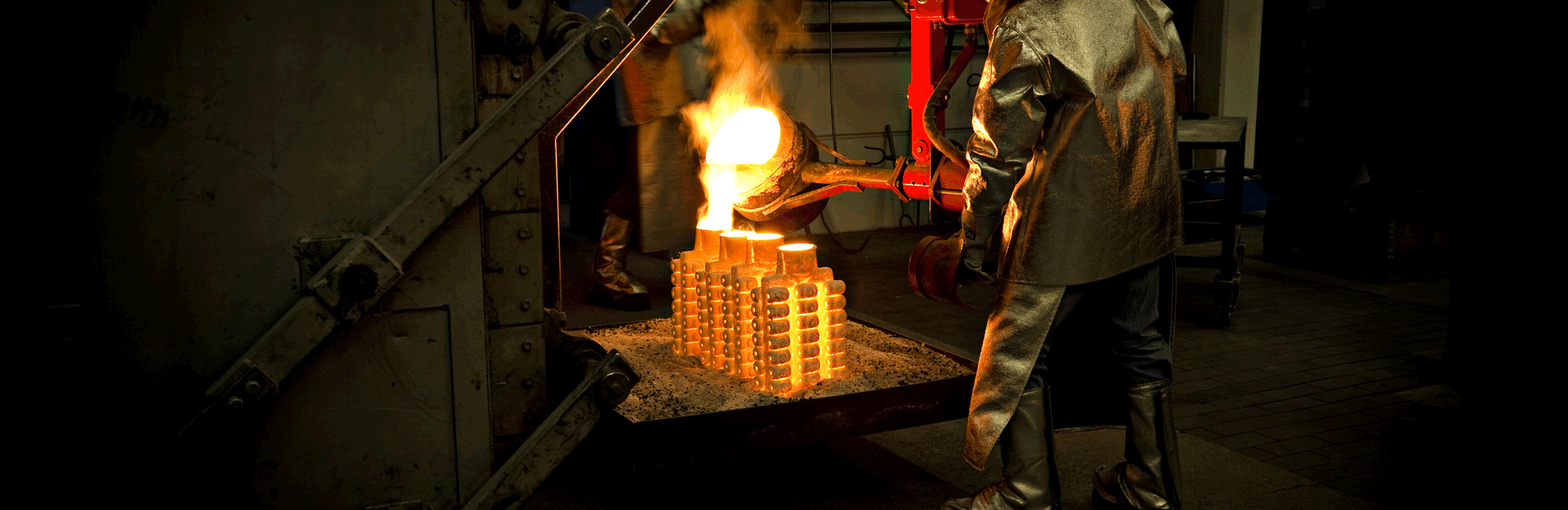
With iron castings weighing from a few grams to several hundred tonnes, casting technology and processes vary greatly. Elkem has a range of alloys to provide the optimum treatment for cast iron whatever the weight and section thickness of your casting.
Elkem’s technical experts can advise you on the right alloy package for all of your casting needs and you can request our brochure on Cast Iron Inoculation via the document request form at the right side of this page.
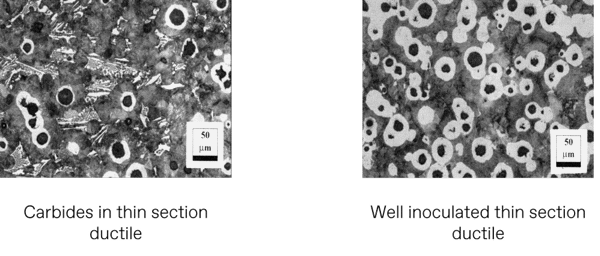
Microstructure of ductile iron castings
Thin section ductile iron castings can be prone to carbide formation due to rapid cooling. This carbide tendency can be measured with thermal analysis and eliminated by using the correct combination of treatment alloys and inoculation.
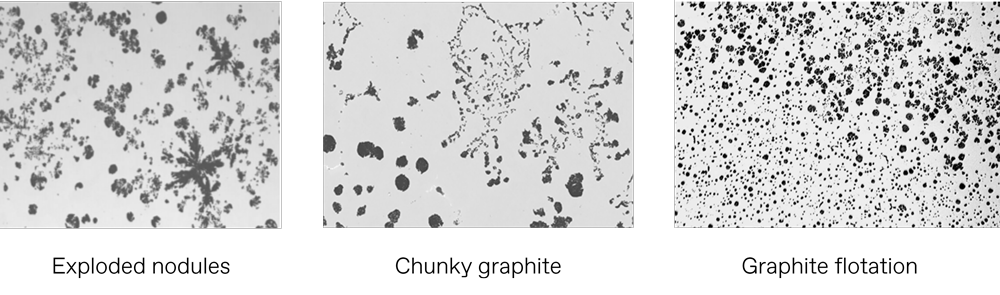
Heavy section ductile iron castings can be prone to exploded nodules, chunky graphite and graphite flotation which reduce mechanical properties. To eliminate these defects, you can use dynamic, customised inoculation to control the point at which graphite precipitation starts during solidification.

Heavy section grey iron castings can be prone to type C (kish) graphite as a result of the slow cooling rate. This can be reduced or eliminated by optimising the carbon equivalent and selecting the correct inoculation practice.
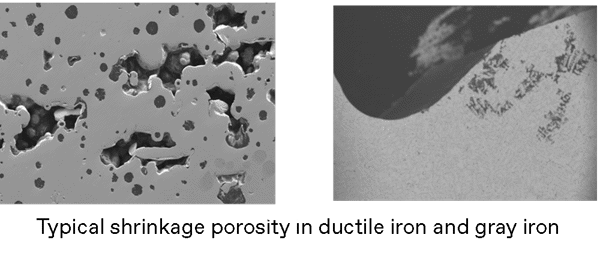
Changes in section thickness
We often see very different casting thicknesses in the same component. The area where the casting section thickness changes can be prone to shrinkage porosity because of the difference in cooling rates.
Section related shrinkage can be minimised by good feeding design characteristics. Optimisation of magnesium treatment and inoculation practices can also considerably reduce the shrinkage tendency of iron.
Acces more examples of technical advice
Contact us
Take your business to the next level by partnering with a world-leading material manufacturer.